Container crisis: how will it affect you?
Maritime transport is essential for the world economy, because according to data from the Post-Pandemic International Logistics report of the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC), 84% of the volume of merchandise traded worldwide travels by sea.
 depositphotos.com
depositphotos.com But recently this type of freight transport has been involved in a series of events that has been called the container crisis .
Have you noticed that lately many products have increased their prices? Perhaps you have seen a variety of articles and consumer goods that even cost twice as much as they previously cost. Well, one of the causes of the increase in products is this so-called crisis of the containers .
In summary: it is not that there is a deficit in the number of containers , but that they are concentrated in a few points and have even been without use for months, thus causing that in other countries, the producing companies that export their goods do not find enough space to transport them. to the destination countries that consume them.
It may interest you: Shortage of supplies and containers could generate shortages on Good End and Christmas.
What is the cause of the container crisis?
After having an idea of what the container crisis consists of , what are the causes of this phenomenon that is affecting the world economy?
-
Restrictions due to the current Covid-19 pandemic. Many boats that transported merchandise were forced to cancel their trips to reduce the rate of infections. This phenomenon of the container crisis occurred mainly on the routes that go from Asia to Europe and America, in both directions.
On the one hand, according to information from the BBC, the vessels that carried merchandise from Asia to America and Europe, had to stay in those destinations without being able to return to Asia with the products they carried from these continents. Due to the cut in maritime traffic, the containers were left stacked and unused in America and Europe.
On the other hand, in China, which has 8 of the 10 most active ports in the world, the shipment of goods to Europe and America had to be stopped, due to the strict measures that were implemented to reduce the contagion of Covid-19.
According to the ECLAC report, the impact of the pandemic on maritime cargo transport activity will imply a setback of more than 3 years, according to the evolution of cargo transported in volume.
-
Typhoon season. Many Chinese ports closed during the typhoon season, increasing the number of vessels and containers detained.
-
Lower production of goods. To avoid the contagion of Covid-19, many oriental factories stopped their operations, which implied a decrease in their production and therefore in the shipment of products, thus reducing the demand for maritime transport.
-
An accident in the Suez Canal. According to the information in the article The day Given blocked maritime transport (published by the University of Deusto), on March 23, 2021 an accident occurred in the Suez Canal, in which the Ever Given super ship was involved. which carried a weight of more than 220 thousand tons in containers.
This vessel, owned by the Taiwanese shipping company Evergreen Marine Corp., was heading from Malaysia to the Netherlands. As it passed through the Suez Canal, it lost control due to its large dimensions, the weight it was carrying and the natural conditions of this single-track canal. The Ever Given ended up totally blocking it, so other boats could not navigate.
The blockade due to the accident lasted 6 days, enough time for it to affect maritime transport, merchandise trade and therefore the world economy, since this channel covers approximately 10% of world trade, as it is the direct connection between Asia. and Europe.
According to information from the aforementioned article, the Suez Authority estimated a preliminary amount of one billion dollars for everything that this accident involved: the transit fees that were lost during the blockade days and the damage to the canal, plus those that accrued due to losses. of the vessels that were detained for 6 days and the costs of repairs to the Suez Canal.
It may interest you: The pandemic increases inequality and poverty in Latin America
A problem that comes even before the pandemic
The fact that containers have been concentrated in just a few lines of companies since before the pandemic is another factor that influenced the current container crisis .
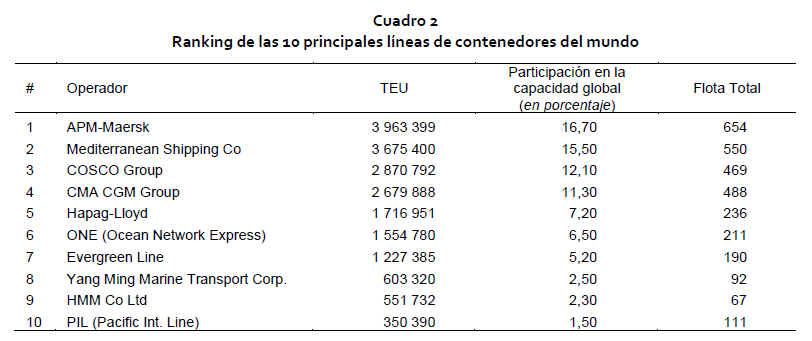
The data from the ECLAC report indicate that 80% of maritime container transport is concentrated in a very small number of large operators.
The process of concentration of the container sector has progressed between mergers and acquisitions: according to the ECLAC count, of the 30 companies that carried most of the world container traffic in 1992, now only three groups control that 80% of the traffic main maritime.
These large groups that control maritime traffic have managed to achieve market power, which has generated pressure on the terminals to reduce the rates of their services.
It might interest you: Inflation: This crisis is just beginning
Who will be most affected by the container crisis?
Given the shortage of space and containers to transport goods, many shipping companies and especially the largest maritime transport companies chose to increase the cost of freight, as this would allow them to compensate for the losses due to the lower demand for their services.
Worldwide there was an average increase of 142% in the prices of ocean freight compared to the costs in 2019. On routes such as the one that go from Shanghai to Los Angeles, this increase reached 199% according to with data from ECLAC.
As mentioned in the same report, and related to the aforementioned historical economic background, the increase in freight costs goes beyond cancellations of freight transport due to port closures. The fact that the container shipping market is based on a system of alliances and consortia allows you to control prices.
The price of ocean freight also increased because the largest importers that resist the increase in the price of freight from shipping companies are renting their own ships to transport their goods, which implies a greater number of ships in transit. That is to say, greater traffic or supply of maritime transport, but little demand due to the limited availability of space and the low production and shipment of products.
It is then that due to the shortage of certain goods, either due to lack of production or lack of transportation, it is expected that their prices will continue to increase and that it will not be possible to meet the estimated demand for items for this end of 2021. And how is it understood , the high prices of the products due to these situations will end up being paid by consumers.
It might interest you: How to undertake in times of crisis
The container crisis will affect certain sectors more
Although consumers are expected to pay the highest prices due to this container crisis , certain companies will also be seriously affected by this phenomenon.
-
Small shipping companies. As seen before, the large shipping companies that can offer overseas services, that is, that have the capacity to transport large freights over long distances, are imposing their rates, which leaves out the small shipping companies , which cannot charge the same rates. Many of these small shipping companies , which according to ECLAC are mainly concentrated in Latin America, will be forced to stop operating due to the low demand for their services.
-
Production companies. Possibly many companies, unable to market their products due to the shortage of transportation, see their production, sales, delivery of products and therefore their profits reduced. Even if they agree to transport with the high rates of ocean freight, their products will increase in prices, so if consumers cannot buy them, sales will be reduced.
-
Small businesses or local stores. Faced with the increase in the price of products, due to the rise in prices in maritime freight, some local or small businesses will not be able to buy these products, so a drop in sales is expected that eventually leads them to find themselves in economic difficulties or even to close. These closures will possibly bring as a consequence a reduction in the jobs generated and a lower consumption capacity.
It might interest you: How to start a business: 10 steps to achieve it
https://www.entrepreneur.com/article/402076