How Google creates knowledge panels
The presence of knowledge panels has been increasing in Google’s SERPs for years. As a result, the classic search results, also known as “10 blue links,” are getting more competition when it comes to attracting the attention of the searcher.
Or should we better call it the “questioners”? Because most search queries are implicitly formulated questions that require an answer.
Google wants to use the SERP features to answer the questions directly. These features are a window into theKnowledge Graph or are directly or indirectly associated with it.
This article will explain how Google creates knowledge panels – and how they work.
What are knowledge panels?
Entities play a direct or indirect role in many search queries. That is why you will find different box variants in the SERPs for many search queries.
As soon as Google recognizes that with a search query as a subject directly after the entity asked about knowledge panel delivered. The knowledge panel can also be called an entity box and it is delivered for almost all entity types.
However, a knowledge panel is not delivered for every entity of a type. The entity must be captured in the Knowledge Graph.
One of the fundamental questions for SEOs is which entities to include in the Google Knowledge Graph. According to Google, only named entities from the classes of the following entity types are primarily recorded in the Knowledge Graph.
- Books and book series
- Educational institutions, government, local shops, companies
- Events
- Movies and film series
- Music groups and albums
- People
- Places
- Sports teams
- TV series
- Video games and series
- Websites or domains
However, not all entities from these classes are associated with a knowledge panel presented in the SERPs. The entities must have a certain social relevance or authority in the respective area.
The classic knowledge panel can be recognized by the share button in the upper area of the panel.

Knowledge panels are not to be confused with business boxes. These are not based on the Knowledge Graph, but on an entry on Google Business. To what extent the data from Google Business is also taken into account in the Knowledge Graph is not clear, but it is not unlikely.
Google uses different templates for the knowledge panel. The placeholders for the content in the knowledge panel vary depending on the entity or entity type that is searched for. The placeholders are based on the standard attributes of the respective entity type.
How does Google determine the relevance of an entity to serve a knowledge panel?
The criteria by which Google evaluates this relevance are not clearly documented or there are no concrete statements from Google.
Wikipedia plays a special role for the proof entity. The surest way to be recognized as an entity is to have an entry on Wikipedia.
But other platforms that provide semi-structured data, such as Soundcloud, can also be used by Google to identify entities, as the hack for the keyword “SEO services India” has shown.
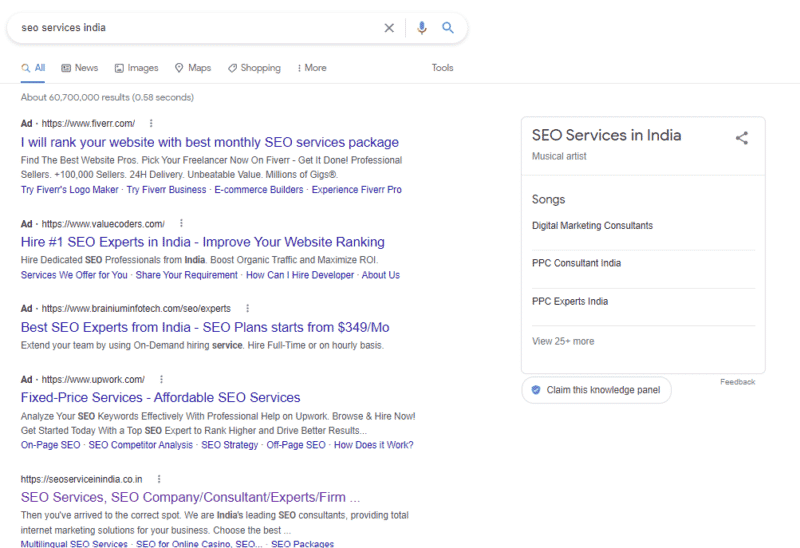
There it becomes clear that SoundCloud was used as the source for the entity detection. Websites such as SoundCloud or Wikipedia always present information in a consistent structure. This means that the information can be easily extracted from the websites without mark-ups.
How does Google create a knowledge panel?
The knowledge panels were first presented in the SERPs with the introduction of the Knowledge Graph in 2012.
In the Google patent Providing knowledge panels with search results, one finds the basic methodology and purpose of the knowledge panel. The purpose for users of a Search engine is described as follows.
“Knowledge panels can improve users’ search experiences, in particular for queries directed to learning, browsing, or discovery. For example, the knowledge panel supplies users with basic factual information or a summary of information about a particular entity referenced in a search query. Knowledge panels can assist users in navigating to relatedcontent in a seamless and natural way. Knowledge panels can supply new content that may not otherwise be encountered by a user without selecting several search results. Knowledge panels can also help users obtain information faster than they would if the users were required to click through multiple search results to obtain the information.”
Here is an excerpt from the patent on the methodology for delivering the knowledge panel:
“Methods, systems, and apparatus, including computer programs encoded on a computer storage medium, for providing knowledge panels with search results. In one aspect, a method includes obtaining search results that are responsive to a received query. A factual entity referenced by the query is identified. Content is identified for display in a knowledge panel for the factual entity. The content includes at least one content item obtained from a first resource and at least one second content item obtained from a second resource different than the first resource. Data is provided that causes the identified search results and the knowledge panel to be presented on a search results page. The knowledge panel presents the identified content in a knowledge panel area that is alongside at least a portion of the search results.”
The basic functionality when delivering a knowledge panel can be summarized in the following process steps:
- Identification of one or more relevant entities in the search query
- Identification of relevant sources for the main
- Creation of relevant search results regarding the search query
- Check whether the search query really refers to the actual main
- entity Determination of an entity type for the main entity requested
- Selection of a suitable knowledge panel template that matches the one determinedEntity Type
- Identification of relevant content elements related to the main entity from a relevant and trusted source.
- Determination of another content element from another source.
- Filling of the placeholders in the selected knowledge panel template with the selected content elements.
- Merging search results and knowledge panel on one search results page
I find it exciting to realize that each entity type is assigned its own knowledge panel template with corresponding placeholders.
The entity type of the respective entity represented by a knowledge panel is always specified below the name of the entity. Depending on which standard attributes are assigned to the entity type and for which attributes the values are available, content is specified in the knowledge panel.
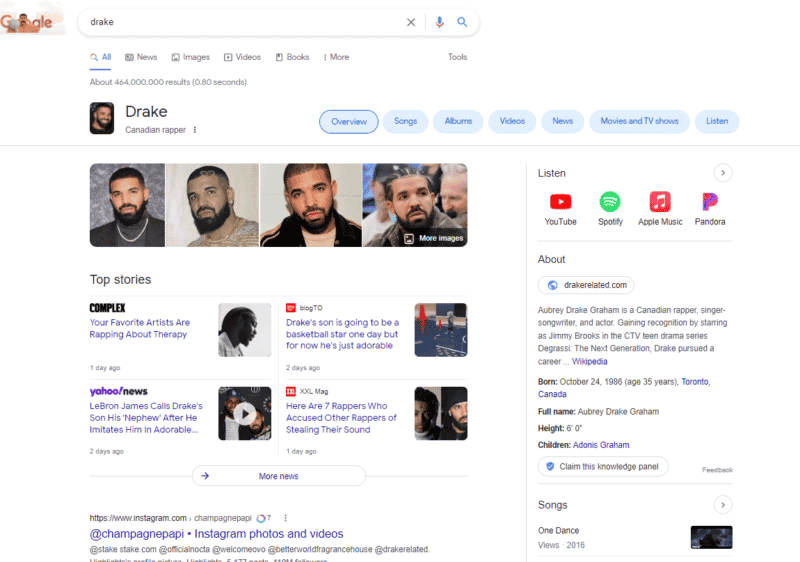
Example entity type “Canadian rapper” in musician Drake’s knowledge panel
How does Google generate images for the knowledge panel?
Regarding the question of which images are selected for the knowledge panel, I looked at some Google patents from the last few years.
Selection of representative images
This patent describes how Google could select representative images for entities of the type “person” for the corresponding knowledge panel.
The steps are as follows:
- Access a selection of possible images
- Cluster by similarity
- Identify the most popular clusters
- Determine whether the image is a portrait or not
- Assigna portrait score
- Select the most representative image
- Display the image in the knowledge panel
The selection of possible images as well as the clustering of these into categories is determined depending on the proximity to the entity as well as the aspect ratio. It will be very likelythat machine learning methods are used. We get an idea of possible categories by looking at the image search.
System and method for associating images with semantic entities
Another exciting Google patent related to images and entities describes how Google Images could assemble the images for semantic pre-selection.
“A system and computer-implemented method for associating images with semantic entities and providing search results using the semantic entities. An image database contains one or more source images associated with one or more images labels. A computer may generate one or more documents containing the labels associated with each image. Analysis may be performed on the one or more documents to associate the source images with semantic entities. The semantic entities may be used to provide search results. In response to receiving a target image as a search query, the target image may be compared with the source images to identify similar images. The semantic entities associated with the similar images may be used to determine a semantic entity for the target image. The semantic entity for the target image may be used to provide search results in response to the search initiated by the target image.”
In this patent, images are labeled with attributes. through which the images can be assigned to specific entities. These attributes are initially identified via image recognition of an initial image. Additional attributes are added via attributes of similar images and similar entities, presumably of the same type. This is how the meaning of the picture emerges.
These patents describe some approaches to how Google could specify images for knowledge panels. In my opinion, the source of the image is also decisive, which image Google selects the most relevant image for an entity and thus uses in the knowledge panel.
Popular sources for people’s pictures seem to include Wikidata, Wikipedia, Wikimedia,social media profiles (e.g., LinkedIn, Twitter) and well-known magazines. To what extent the ranking in the image search correlates with the selection of the image(s) for the knowledge panel is unclear.
The influence of the Knowledge Graph is growing fast
The influence of SERP features is increasing every year and with it the influence of the Knowledge Graph on the search results. The classic blue links are losing more attention and thus relevance.
Entities are at the center of the Knowledge Graph and will have an increasing impact on the SERPs.
With regard to voice search, SERP features such as featured snippets and knowledge panels also play an important role.
The changes in the SERPs due to the MUM update can already be seen, as can the increasingly central role of entity-based searches.
Therefore, SEOs should no longer perceive this topic as a “nice-to-have.” The Knowledge Graph should be included in your SEO strategies.
Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
New on Search Engine Land
https://searchengineland.com/how-google-creates-knowledge-panels-386025
