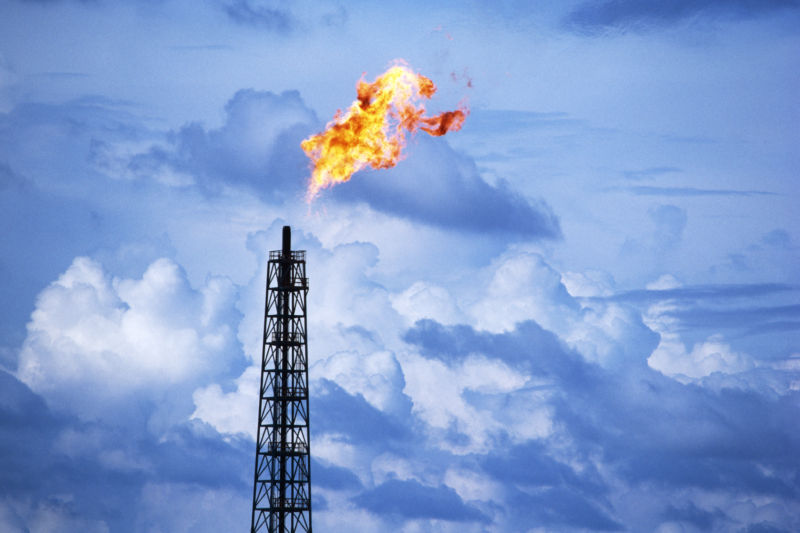
Enlarge / In some cases, stray methane is burned to limit how much escapes into the atmosphere. (credit: Lawrence Berkeley Lab)
The Trump administration has been working to rollback rules instated by the Obama administration that would limit how much methane gas could be vented to the atmosphere at oil- and gas-drilling and processing operations. In a press release today, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) announced that it is proposing to relax Obama-era rules, saving the industry $484 million in avoided energy costs.
But the EPA is expected to justify its rules with analysis. That analysis (PDF) suggests that this regulatory rollback will also come with costs in the form of 308,000 short tons of methane emitted between 2019 and 2025. For context, the Aliso Canyon gas leak three years ago represented the largest accidental release of methane in US history, and over the four months that workers struggled to plug that well, 107,000 short tons of methane are estimated to have been released.
That is a serious amount of methane with serious climate consequences in the short-run. Methane is many times more potent than CO2 as a greenhouse gas, though it decomposes in the atmosphere more quickly. Carbon dioxide sticks around in the atmosphere for a longer time, but each individual molecule of CO2 has less of a warming effect than a molecule of methane.
Read 5 remaining paragraphs | Comments
https://arstechnica.com/?p=1371751