
Windows 11’s big feature update in September included a long list of minor changes, plus the Copilot AI assistant; that update was followed by Windows 11 23H2 in late October, which reset the operating system’s timeline for technical support and security updates but didn’t add much else in and of itself. But Windows development never stops these days, and this month’s Insider Preview builds have already shown us a few things that could end up in the stable version of the operating system in the next couple of months.
One major addition, which rolled out to Dev Channel builds on January 11 and Beta Channel builds today, is support for 80Gbps USB 4 ports. These speeds are part of the USB4 Version 2.0 spec—named with the USB-IF’s typical flair for clarity and consistency—that was published in 2022. Full 80Gbps speeds are still rare and will be for the foreseeable future, but Microsoft says that they’ll be included the Razer Blade 18 and a handful of other PCs with Intel’s 14th-generation HX-series laptop processors. We’d expect the new speeds to proliferate slowly and mostly in high-end systems over the next few months and years.
Another addition to that January 11 Dev Channel build is a change in how the Copilot generative AI assistant works. Normally, Copilot is launched by the user manually, either by clicking the icon on the taskbar, hitting the Win+C key combo, or (in some new PCs) by using the dedicated Copilot button on the keyboard. In recent Dev Channel builds, the Copilot window will open automatically on certain PCs as soon as you log into Windows, becoming part of your default desktop unless you turn it off in Settings.
The Copilot panel will only open by default on screens that meet minimum size and resolution requirements, things that Windows already detects and takes into account when setting your PC’s default zoom and showing available Snap Layouts, among other things. Microsoft says it’s testing the feature on screens that are 27 inches or larger with 1,920 or more horizontal pixels (for most screens, this means a minimum resolution of 1080p). For PCs without Copilot, including those that haven’t been signed into a Microsoft account, the feature will continue to be absent.
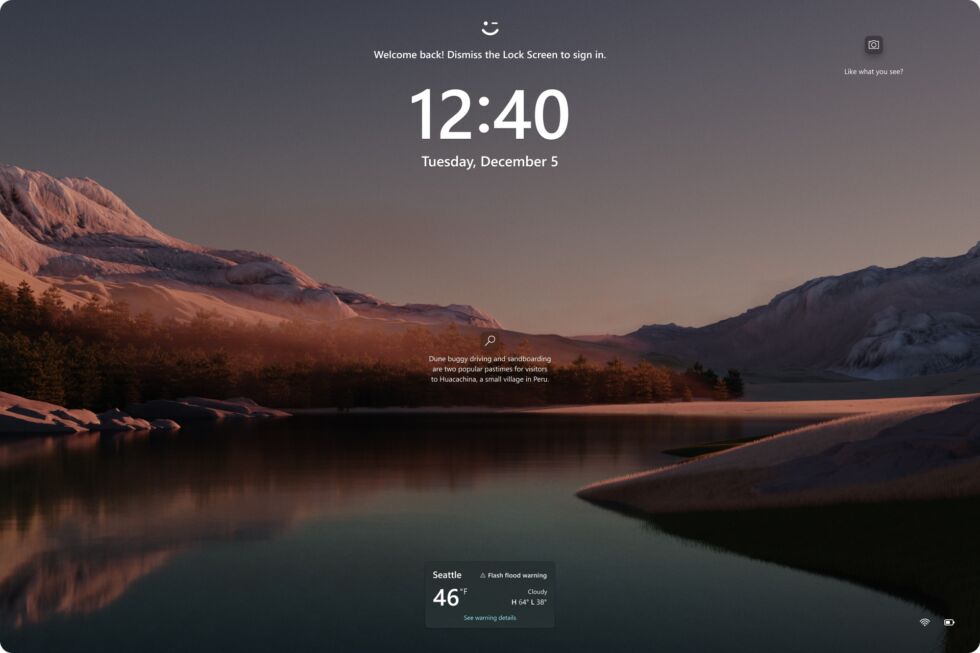
Other additions to the Dev Channel builds this month include easy Snipping Tool editing for Android screenshots from phones that have been paired to your PC, custom user-created voice commands, the ability to share URLs directly to services like WhatsApp and Gmail from the Windows share window, a new Weather widget for the Windows lock screen, and app install notifications from the Microsoft store.
Microsoft hasn’t publicized any of the changes it has made to its Canary channel builds since January 4—this is typical since it changes the fastest, and the tested features are the most likely to be removed or significantly tweaked before being released to the public. Most of the significant additions from that announcement have since made it out to the other channels, but there are a couple of things worth noting. First, there’s a new Energy Saver taskbar icon for desktop PCs without batteries, making it easier to tell when the feature is on without creating confusion. And the venerable WordPad app, originally marked for deletion in September, has also been removed from these builds and can’t be reinstalled.
Microsoft doesn’t publish Windows feature updates on an exact cadence beyond its commitment to deliver one with a new version number once per year in the fall. Last year’s first major batch of Windows 11 additions rolled out at the end of February, so a late winter or early spring launch window for the next batch of features could make sense.
https://arstechnica.com/?p=1997547

