It’s all wrong
It always was. Most of us knew it. But with limited resources, we just couldn’t really compare the quality, size, and speed of link indexes very well. Frankly, most backlink index comparisons would barely pass for a high school science fair project, much less a rigorous peer review.
My most earnest attempt at determining the quality of a link index was back in 2015, before I joined Moz as Principal Search Scientist. But I knew at the time that I was missing a huge key to any study of this sort that hopes to call itself scientific, authoritative or, frankly, true: a random, uniform sample of the web.
But let me start with a quick request. Please take the time to read this through. If you can’t today, schedule some time later. Your businesses depend on the data you bring in, and this article will allow you to stop taking data quality on faith alone. If you have questions with some technical aspects, I will respond in the comments, or you can reach me on twitter at
@rjonesx. I desperately want our industry to finally get this right and to hold ourselves as data providers to rigorous quality standards.
Quick links:
- Home
- Getting it right
- What’s the big deal with random?
- Now what? Defining metrics
- Caveats
- The metrics dashboard
- Size matters
- Speed
- Quality
- The Link Index Olympics
- What’s next?
- About PA and DA
- Quick takeaways
Getting it right
One of the greatest things Moz offers is a leadership team that has given me the freedom to do what it takes to “get things right.” I first encountered this when Moz agreed to spend an enormous amount of money on clickstream data so we could make our keyword tool search volume better (a huge, multi-year financial risk with the hope of improving literally one metric in our industry). Two years later, Ahrefs and SEMRush now use the same methodology because it’s just the right way to do it.
About 6 months into this multi-year project to replace our link index with the huge Link Explorer, I was tasked with the open-ended question of “how do we know if our link index is good?” I had been thinking about this question ever since that article published in 2015 and I knew I wasn’t going to go forward with anything other than a system that begins with a truly “random sample of the web.” Once again, Moz asked me to do what it takes to “get this right,” and they let me run with it.
What’s the big deal with random?
It’s really hard to over-state how important a good random sample is. Let me diverge for a second. Let’s say you look at a survey that says 90% of Americans believe that the Earth is flat. That would be a terrifying statistic. But later you find out the survey was taken at a Flat-Earther convention and the 10% who disagreed were employees of the convention center. This would make total sense. The problem is the sample of people surveyed wasn’t of random Americans — instead, it was biased because it was taken at a Flat-Earther convention.
Now, imagine the same thing for the web. Let’s say an agency wants to run a test to determine which link index is better, so they look at a few hundred sites for comparison. Where did they get the sites? Past clients? Then they are probably biased towards SEO-friendly sites and not reflective of the web as a whole. Clickstream data? Then they would be biased towards popular sites and pages — once again, not reflective of the web as a whole!
Starting with a bad sample guarantees bad results.
It gets even worse, though. Indexes like Moz report our total statistics (number of links or number of domains in our index). However, this can be terribly misleading. Imagine a restaurant which claimed to have the largest wine selection in the world with over 1,000,000 bottles. They could make that claim, but it wouldn’t be useful if they actually had 1,000,000 of the same type, or only Cabernet, or half-bottles. It’s easy to mislead when you just throw out big numbers. Instead, it would be much better to have a random selection of wines from the world and measure if that restaurant has it in stock, and how many. Only then would you have a good measure of their inventory. The same is true for measuring link indexes — this is the theory behind my methodology.
Unfortunately, it turns out getting a random sample of the web is really hard. The first intuition most of us at Moz had was to just take a random sample of the URLs in our own index. Of course we couldn’t — that would bias the sample towards our own index, so we scrapped that idea. The next thought was: “We know all these URLs from the SERPs we collect — perhaps we could use those.” But we knew they’d be biased towards higher-quality pages. Most URLs don’t rank for anything — scratch that idea. It was time to take a deeper look.
I fired up Google Scholar to see if any other organizations had attempted this process and found literally one paper, which Google produced back in June of 2000, called “On Near-Uniform URL Sampling.” I hastily whipped out my credit card to buy the paper after reading just the first sentence of the abstract: “We consider the problem of sampling URLs uniformly at random from the Web.” This was exactly what I needed.
Why not Common Crawl?
Many of the more technical SEOs reading this might ask why we didn’t simply select random URLs from a third-party index of the web like the fantastic Common Crawl data set. There were several reasons why we considered, but chose to pass, on this methodology (despite it being far easier to implement).
- We can’t be certain of Common Crawl’s long-term availability. Top million lists (which we used as part of the seeding process) are available from multiple sources, which means if Quantcast goes away we can use other providers.
- We have contributed crawl sets in the past to Common Crawl and want to be certain there is no implicit or explicit bias in favor of Moz’s index, no matter how marginal.
- The Common Crawl data set is quite large and would be harder to work with for many who are attempting to create their own random lists of URLs. We wanted our process to be reproducible.
How to get a random sample of the web
The process of getting to a “random sample of the web” is fairly tedious, but the general gist of it is this. First, we start with a well-understood biased set of URLs. We then attempt to remove or balance this bias out, making the best pseudo-random URL list we can. Finally, we use a random crawl of the web starting with those pseudo-random URLs to produce a final list of URLs that approach truly random. Here are the complete details.
1. The starting point: Getting seed URLs
The first big problem with getting a random sample of the web is that there is no true random starting point. Think about it. Unlike a bag of marbles where you could just reach in and blindly grab one at random, if you don’t already know about a URL, you can’t pick it at random. You could try to just brute-force create random URLs by shoving letters and slashes after each other, but we know language doesn’t work that way, so the URLs would be very different from what we tend to find on the web. Unfortunately, everyone is forced to start with some pseudo-random process.
We had to make a choice. It was a tough one. Do we start with a known strong bias that doesn’t favor Moz, or do we start with a known weaker bias that does? We could use a random selection from our own index for the starting point of this process, which would be pseudo-random but could potentially favor Moz, or we could start with a smaller, public index like the Quantcast Top Million which would be strongly biased towards good sites.
We decided to go with the latter as the starting point because Quantcast data is:
- Reproducible. We weren’t going to make “random URL selection” part of the Moz API, so we needed something others in the industry could start with as well. Quantcast Top Million is free to everyone.
- Not biased towards Moz: We would prefer to err on the side of caution, even if it meant more work removing bias.
- Well-known bias: The bias inherent in the Quantcast Top 1,000,000 was easily understood — these are important sites and we need to remove that bias.
- Quantcast bias is natural: Any link graph itself already shares some of the Quantcast bias (powerful sites are more likely to be well-linked)
With that in mind, we randomly selected 10,000 domains from the Quantcast Top Million and began the process of removing bias.
2. Selecting based on size of domain rather than importance
Since we knew the Quantcast Top Million was ranked by traffic and we wanted to mitigate against that bias, we introduced a new bias based on the size of the site. For each of the 10,000 sites, we identified the number of pages on the site according to Google using the “site:” command and also grabbed the top 100 pages from the domain. Now we could balance the “importance bias” against a “size bias,” which is more reflective of the number of URLs on the web. This was the first step in mitigating the known bias of only high-quality sites in the Quantcast Top Million.
3. Selecting pseudo-random starting points on each domain
The next step was randomly selecting domains from that 10,000 with a bias towards larger sites. When the system selects a site, it then randomly selects from the top 100 pages we gathered from that site via Google. This helps mitigate the importance bias a little more. We aren’t always starting with the homepage. While these pages do tend to be important pages on the site, we know they aren’t always the MOST important page, which tends to be the homepage. This was the second step in mitigating the known bias. Lower-quality pages on larger sites were balancing out the bias intrinsic to the Quantcast data.
4. Crawl, crawl, crawl
And here is where we make our biggest change. We actually crawl the web starting with this set of pseudo-random URLs to produce the actual set of random URLs. The idea here is to take all the randomization we have built into the pseudo-random URL set and let the crawlers randomly click on links to produce the truly random URL set. The crawler will select a random link from our pseudo-random crawlset and then start a process of randomly clicking links, each time with a 10% chance of stopping and a 90% chance of continuing. Wherever the crawler ends, the final URL is dropped into our list of random URLs. It is this final set of URLs that we use to run our metrics. We generate around 140,000 unique URLs through this process monthly to produce our test data set.
Phew, now what? Defining metrics
Once we have the random set of URLs, we can start really comparing link indexes and measuring their quality, quantity, and speed. Luckily, in their quest to “get this right,” Moz gave me generous paid access to competitor APIs. We began by testing Moz, Majestic, Ahrefs, and SEMRush, but eventually dropped SEMRush after their partnership with Majestic.
So, what questions can we answer now that we have a random sample of the web? This is the exact wishlist I sent out in an email to leaders on the link project at Moz:
- Size:
- What is the likelihood a randomly selected URL is in our index vs. competitors?
- What is the likelihood a randomly selected domain is in our index vs. competitors?
- What is the likelihood an index reports the highest number of backlinks for a URL?
- What is the likelihood an index reports the highest number of root linking domains for a URL?
- What is the likelihood an index reports the highest number of backlinks for a domain?
- What is the likelihood an index reports the highest number of root linking domains for a domain?
- Speed:
- What is the likelihood that the latest article from a randomly selected feed is in our index vs. our competitors?
- What is the average age of a randomly selected URL in our index vs. competitors?
- What is the likelihood that the best backlink for a randomly selected URL is still present on the web?
- What is the likelihood that the best backlink for a randomly selected domain is still present on the web?
- Quality:
- What is the likelihood that a randomly selected page’s index status (included or not included in index) in Google is the same as ours vs. competitors?
- What is the likelihood that a randomly selected page’s index status in Google SERPs is the same as ours vs. competitors?
- What is the likelihood that a randomly selected domain’s index status in Google is the same as ours vs. competitors?
- What is the likelihood that a randomly selected domain’s index status in Google SERPs is the same as ours vs. competitors?
- How closely does our index compare with Google’s expressed as “a proportional ratio of pages per domain vs our competitors”?
- How well do our URL metrics correlate with US Google rankings vs. our competitors?
Reality vs. theory
Unfortunately, like all things in life, I had to make some cutbacks. It turns out that the APIs provided by Moz, Majestic, Ahrefs, and SEMRush differ in some important ways — in cost structure, feature sets, and optimizations. For the sake of politeness, I am only going to mention name of the provider when it is Moz that was lacking. Let’s look at each of the proposed metrics and see which ones we could keep and which we had to put aside…
- Size: We were able monitor all 6 of the size metrics!
- Speed:
- We were able to include this Fast Crawl metric.
- What is the average age of a randomly selected URL in our index vs. competitors?
Getting the age of a URL or domain is not possible in all APIs, so we had to drop this metric. - What is the likelihood that the best backlink for a randomly selected URL is still present on the web?
Unfortunately, doing this at scale was not possible because one API is cost prohibitive for top link sorts and another was extremely slow for large sites. We hope to run a set of live-link metrics independently from our daily metrics collection in the next few months. - What is the likelihood that the best backlink for a randomly selected Domain is still present on the web?
Once again, doing this at scale was not possible because one API is cost prohibitive for top link sorts and another was extremely slow for large sites. We hope to run a set of live-link metrics independently from our daily metrics collection in the next few months.
- Quality:
- We were able to keep this metric.
- What is the likelihood that a randomly selected page’s index status in Google SERPs is the same as ours vs. competitors?
Chose not to pursue due to internal API needs, looking to add soon. - We were able to keep this metric.
- What is the likelihood that a randomly selected domain’s index status in Google SERPs is the same as ours vs. competitors?
Chose not to pursue due to internal API needs at the beginning of project, looking to add soon. - How closely does our index compare with Google’s expressed as a proportional ratio of pages per domain vs our competitors?
Chose not to pursue due to internal API needs. Looking to add soon. - How well do our URL metrics correlate with US Google rankings vs. our competitors?
Chose not to pursue due to known fluctuations in DA/PA as we radically change the link graph. The metric would be meaningless until the index became stable.
Ultimately, I wasn’t able to get everything I wanted, but I was left with 9 solid, well-defined metrics.
On the subject of live links:
In the interest of being TAGFEE, I will openly admit that I think our index has more deleted links than others like the Ahrefs Live Index. As of writing, we have about 30 trillion links in our index, 25 trillion we believe to be live, but we know that some proportion are likely not. While I believe we have the most live links, I don’t believe we have the highest proportion of live links in an index. That honor probably does not go to Moz. I can’t be certain because we can’t test it fully and regularly, but in the interest of transparency and fairness, I felt obligated to mention this. I might, however, devote a later post to just testing this one metric for a month and describe the proper methodology to do this fairly, as it is a deceptively tricky metric to measure. For example, if a link is retrieved from a chain of redirects, it is hard to tell if that link is still live unless you know the original link target. We weren’t going to track any metric if we couldn’t “get it right,” so we had to put live links as a metric on hold for now.
Caveats
Don’t read any more before reading this section. If you ask a question in the comments that shows you didn’t read the Caveats section, I’m just going to say “read the Caveats section.” So here goes…
- This is a comparison of data that comes back via APIs, not within the tools themselves. Many competitors offer live, fresh, historical, etc. types of indexes which can differ in important ways. This is just a comparison of API data using default settings.
- We set the API flags to remove any and all known Deleted Links from Moz metrics but not competitors. This actually might bias the results in favor of competitors, but we thought it would be the most honest way to represent our data set against more conservative data sets like Ahrefs Live.
- Some metrics are hard to estimate, especially like “whether a link is in the index,” because no API — not even Moz — has a call that just tells you whether they have seen the link before. We do our best, but any errors here are on the the API provider. I think we (Moz, Majestic, and Ahrefs) should all consider adding an endpoint like this.
- Links are counted differently. Whether duplicate links on a page are counted, whether redirects are counted, whether canonicals are counted (which Ahrefs just changed recently), etc. all affect these metrics. Because of this, we can’t be certain that everything is apples-to-apples. We just report the data at face value.
- Subsequently, the most important takeaway in all of these graphs and metrics is direction. How are the indexes moving relative to one another? Is one catching up, is another falling behind? These are the questions best answered.
- The metrics are adversarial. For each random URL or domain, a link index (Moz, Majestic, or Ahrefs) gets 1 point for being the biggest, for tying with the biggest, or for being “correct.” They get 0 points if they aren’t the winner. This means that the graphs won’t add up to 100 and it also tends to exaggerate the differences between the indexes.
- Finally, I’m going to show everything, warts and all, even when it was my fault. I’ll point out why some things look weird on graphs and what we fixed. This was a huge learning experience and I am grateful for the help I received from the support teams at Majestic and Ahrefs who, as a customer, responded to my questions honestly and openly.
The metrics dashboard
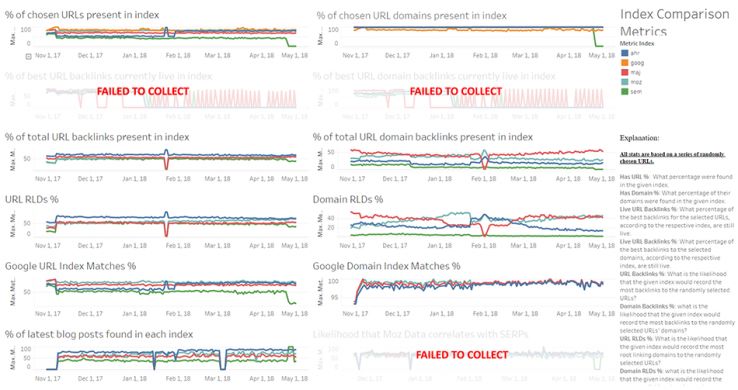 We’ve been tracking these 9 core metrics (albeit with improvements) since November of 2017. With a close eye on quality, size, and speed, we have methodically built an amazing backlink index, not driven by broad counts but instead by intricately defined and measured metrics. Let’s go through each of those metrics now.
We’ve been tracking these 9 core metrics (albeit with improvements) since November of 2017. With a close eye on quality, size, and speed, we have methodically built an amazing backlink index, not driven by broad counts but instead by intricately defined and measured metrics. Let’s go through each of those metrics now.
Size matters
It does. Let’s admit it. The diminutive size of the Mozscape index has been a limitation for years. Maybe someday we will write a long post about all the efforts Moz has made to grow the index and what problems stood in our way, but that’s a post for a different day. The truth is, as much as quality matters, size is huge for a number of specific use-cases for a link index. Do you want to find all your bad links? Bigger is better. Do you want to find a lot of link opportunities? Bigger is better. So we came up with a number of metrics to help us determine where we were relative to our competitors. Here are each of our Size metrics.
Index Has URL
What is the likelihood a randomly selected URL is in our index vs. competitors?
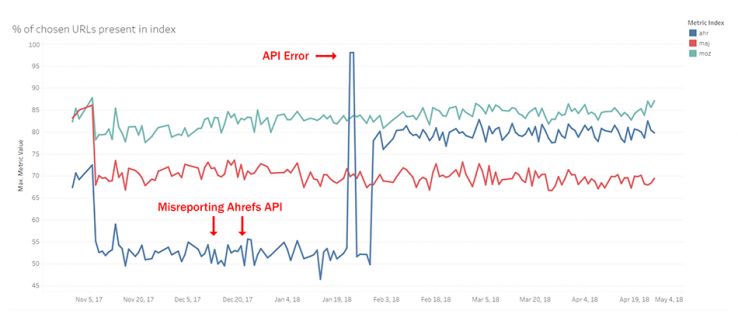
This is one of my favorite metrics because I think it’s a pure reflection of index size. It answers the simple question of “if we grabbed a random URL on the web, what’s the likelihood an index knows about it?” However, you can see my learning curve in the graph (I was misreporting the Ahrefs API due to an error on my part) but once corrected, we had a nice reflection of the indexes. Let me restate this — these are comparisons in APIs, not in the web tools themselves. If I recall correctly, you can get more data out of running reports in Majestic, for example. However, I do think this demonstrates that Moz’s new Link Explorer is a strong contender, if not the largest, as we have led in this category every day except one. As of writing this post, Moz is winning.
Index Has Domain
What is the likelihood a randomly selected domain is in our index vs competitors?
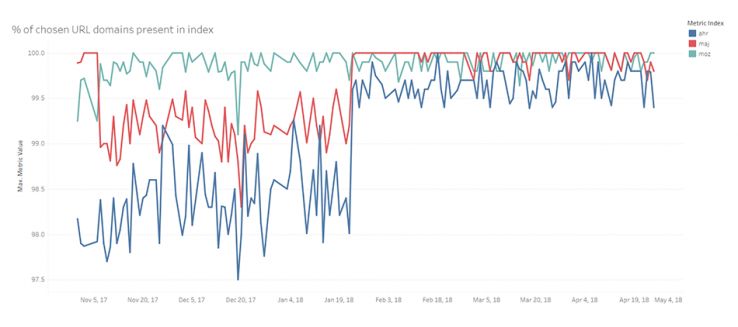
When I said I would show “warts and all,” I meant it. Determining whether a domain is in an index isn’t as simple as you would think. For example, perhaps a domain has pages in the index, but not the homepage. Well, it took me a while to figure this one out, but by February of this year I had it down.
The scale of this graph is important to note as well. The variation is between 99.4 and 100% between Moz, Majestic, and Ahrefs over the last few months. This indicates just how close the link indexes are in terms of knowing about root domains. Majestic has historically tended to win this metric with near 100% coverage, but you would have to select 100 random domains to find one that Moz or Ahrefs doesn’t have information on. However, Moz’s continued growth has allowed us to catch up. While the indexes are super close, as of writing this post, Moz is winning.
Backlinks Per URL
Which index has the highest backlink count for a randomly selected URL?
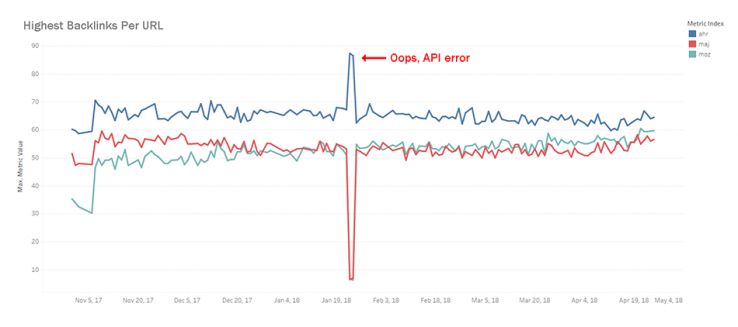
This is a difficult metric to really pin down. Unfortunately, it isn’t easy to determine what backlinks should count and what shouldn’t. For example, imagine a URL has one page linking to it, but that page includes that link 100 times. Is that 100 backlinks or one? Well, it turns out that the different link indexes probably measure these types of scenarios differently and getting an exact definition out of each is like pulling teeth because the definition is so complicated and there are so many edge cases. At any rate, I think this is a great example of where we can show the importance of direction. Whatever the metrics actually are, Moz and Majestic are catching up to Ahrefs, which has been the leader for some time. As of writing this post, Ahrefs is winning.
Root Linking Domains Per URL
Which index reports the highest RLD count for a randomly selected URL?
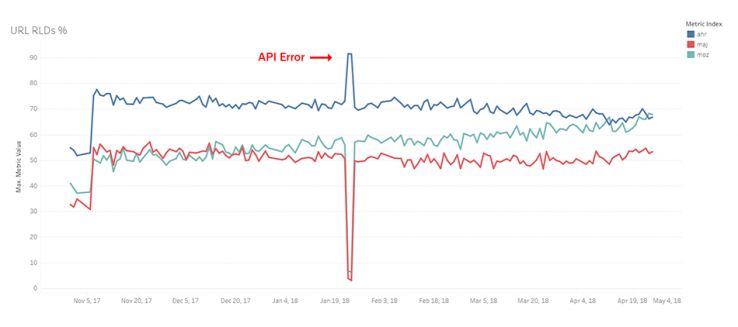
Simple, right? No, even this metric has its nuances. What is a root linking domain? Do subdomains count if they are on subdomain sites like Blogspot or WordPress.com? If so, how many sites are there on the web which should be treated this way? We used a machine learned methodology based on surveys, SERP data, and unique link data to determine our list, but each competitor does it differently. Thus, for this metric, direction really matters. As you can see, Moz has been steadily catching up and as of writing today, Moz is finally winning.
Backlinks Per Domain
Which index reports the highest backlink count for a randomly selected domain?
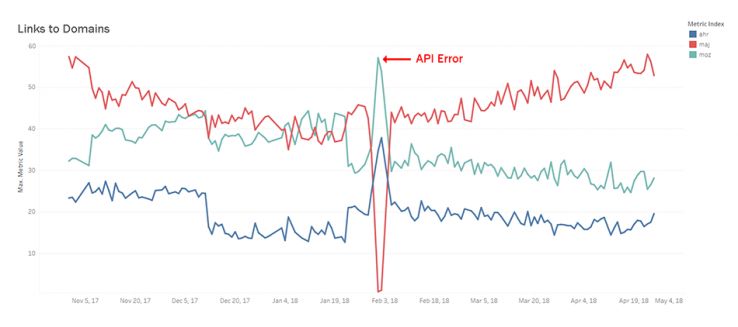
This metric was not kind to me, as I found a terrible mistake early on. (For the other techies reading this, I was storing backlink counts as INT(11) rather than BIGINT, which caused lots of ties for big domains when they were larger than the maximum number size because the database defaults to same highest number.) Nevertheless, Majestic has been stealing the show on this metric for a little while, although the story is deeper than that. Their dominance is such an outlier that it needs to be explained.
One of the hardest decisions a company has to make regarding its backlink index is how to handle spam. On one hand, spam is expensive to the index and probably ignored by Google. On the other hand, it is important for users to know if they have received tons of spammy links. I don’t think there is a correct answer to this question; each index just has to choose. A close examination of the reason why Majestic is winning (and continuing to increase their advantage) is because of a particularly nefarious Wikipedia-clone spam network. Any site with any backlinks from Wikipedia are getting tons of links from this network, which is causing their backlink counts to increase rapidly. If you are worried about these types of links, you need to go take a look at Majestic and look for links ending in primarily .space or .pro, including sites like tennis-fdfdbc09.pro, troll-warlord-64fa73ba.pro, and badminton-026a50d5.space. As of my last tests, there are over 16,000 such domains in this spam network within Majestic’s index. Majestic is winning this metric, but for purposes other than finding spam networks, it might not be the right choice.
Linking Root Domains Per Domain
Which index reports the highest LRD count for a randomly selected domain?
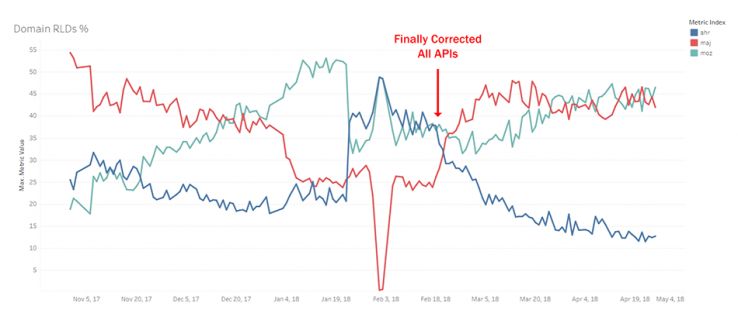
OK, this one took me a while to get just right. In the middle of this graph, I corrected an important error where I was looking at domains only for the root domain on Ahrefs rather than the root domain and all subdomains. This was unfair to Ahrefs until I finally got everything corrected in February. Since then, Moz has been aggressively growing its index, Majestic has picked up LRD counts through the previously discussed network but steadied out, and Ahrefs has remained relatively steady in size. Because of the “adversarial” nature of these metrics, it gives the false appearance that Ahrefs is dropping dramatically. They aren’t. They are still huge, and so is Majestic. The real takeaway is directional: Moz is growing dramatically relative to their networks. As of writing this post, Moz is winning.
Speed
Being the “first to know” is an important part in almost any industry and with link indexes it is no different. You want to know as soon as possible when a link goes up or goes down and how good that link is so you can respond if necessary. Here is our current speed metric.
FastCrawl
What is the likelihood the latest post from a randomly selected set of RSS feeds is indexed?
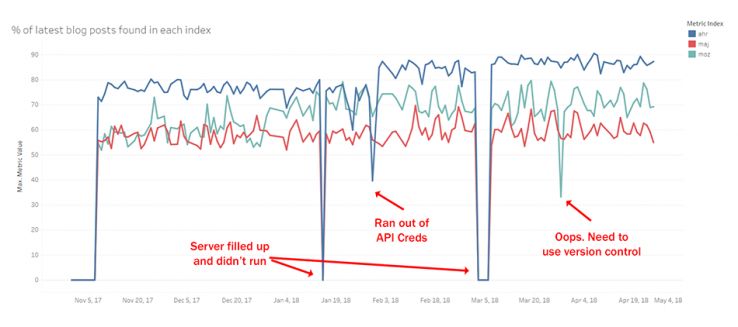
Unlike the other metrics discussed, the sampling here is a little bit different. Instead of using the randomization above, we make a random selection from a million+ known RSS feeds to find their latest post and check to see if they have been included in the various indexes of Moz and competitors. While there are a few errors in this graph, I think there is only one clear takeaway. Ahrefs is right about their crawlers. They are fast and they are everywhere. While Moz has increased our coverage dramatically and quickly, it has barely put a dent in this FastCrawl metric.
Now you may ask, if Ahrefs is so much faster at crawling, how can Moz catch up? Well, there are a couple of answers, but probably the biggest is that new URLs only represent a fraction of the web. Most URLs aren’t new. Let’s say two indexes (one new, one old) have a bunch of URLs they’re considering crawling. Both might prioritize URLs on important domains that they’ve never seen before. For the larger, older index, that will be a smaller percentage of that group because they have been crawling fast a long time. So, during the course of the day, a higher percentage of the old index’s crawl will be dedicated to re-crawl pages it already knows about. The new index can dedicate more of its crawl potential to new URLs.
It does, however, put the pressure on Moz now to improve crawl infrastructure as we catch up to and overcome Ahrefs in some size metrics. As of this post, Ahrefs is winning the FastCrawl metric.
Quality
OK, now we’re talking my language. This is the most important stuff, in my opinion. What’s the point of making a link graph to help people with SEO if it isn’t similar to Google? While we had to cut some of the metrics temporarily, we did get a few in that are really important and worth taking a look.
Domain Index Matches
What is the likelihood a random domain shares the same index status in Google and a link index?
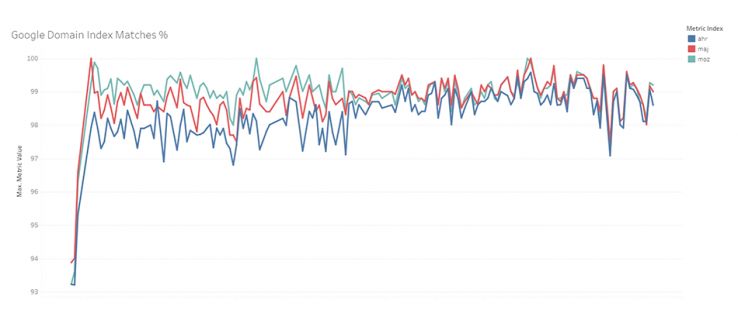 Domain Index Matches seeks to determine when a domain shares the same index status with Google as it does in one of the competing link indexes. If Google ignores a domain, we want to ignore a domain. If Google indexes a domain, we want to index a domain. If we have a domain Google doesn’t, or vice versa, that is bad.
Domain Index Matches seeks to determine when a domain shares the same index status with Google as it does in one of the competing link indexes. If Google ignores a domain, we want to ignore a domain. If Google indexes a domain, we want to index a domain. If we have a domain Google doesn’t, or vice versa, that is bad.
This graph is a little harder to read because of the scale (the first few days of tracking were failures), but what we actually see is a statistically insignificant difference between Moz and our competitors. We can make it look more competitive than it really is if we just calculate wins and losses, but we have to take into account an error in the way we determined Ahrefs index status up until around February. To do this, I show wins/losses for all time vs. wins/losses over the last few months.
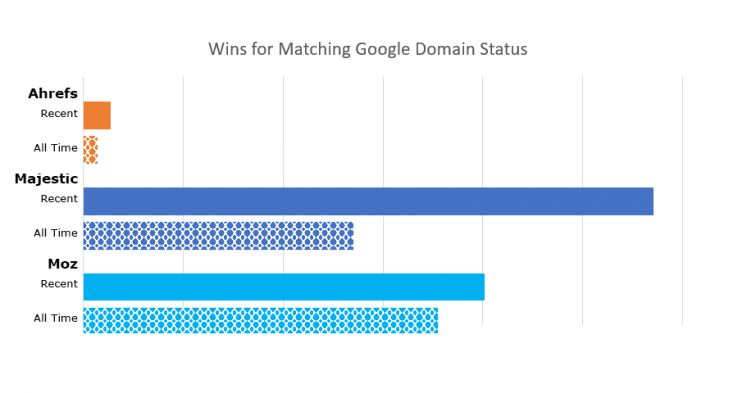
As you can see, Moz wins the “all time,” but Majestic has been winning more over the last few months. Nevertheless, these are quite insignificant, often being the difference between one or two domain index statuses out of 100. Just like the Index Has Domain metric we discussed above, nearly every link index has nearly every domain, and looking at the long-term day-by-day graph shows just how incredibly close they are. However, if we are keeping score, as of today (and the majority of the last week), Moz is winning this metric.
Domain URL Matches
What is the likelihood a random URL shares the same index status in Google as in a link index?
This one is the most important quality metric, in my honest opinion. Let me explain this one a little more. It’s one thing to say that your index is really big and has lots of URLs, but does it look like Google’s? Do you crawl the web like Google? Do you ignore URLs Google ignores while crawling URLs that Google crawls? This is a really important question and sets the foundation for a backlink index that is capable of producing good relational metrics like PA and DA.
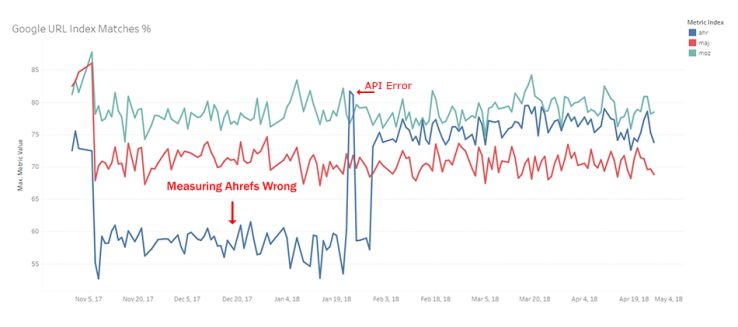
This is one of the metrics where Moz just really shines. Once we corrected for an error in the way we were checking Ahrefs, we could accurately determine whether our index was more or less like Google’s than our competitors. Since the beginning of tracking, Moz Link Explorer has never been anything but #1. In fact, we only had 3 ties with Ahrefs and never lost to Majestic. We have custom-tailored our crawl to be as much like Google as possible, and it has paid off. We ignore the types of URLs Google hates, and seek out the URLs Google loves. We believe this will pay huge dividends in the long run for our customers as we expand our feature set based on an already high-quality, huge index.
The Link Index Olympics
Alright, so we’ve just spent a lot of time delving into these individual metrics, so I think it’s probably worth it to put these things into an easy-to-understand context. Let’s pretend for a moment that this is the Link Index Olympics, and no matter how much you win or lose by, it determines whether you receive a gold, bronze or silver medal. I’m writing this on Wednesday, April 25th. Let’s see how things play out if the Olympics happened today:

As you can see, Moz takes the gold in six of the nine metrics we measure, two silvers, and one bronze. Moreover, we’re continuing to grow and improve our index daily. As most of the above graphs indicate, we tend to be improving relative to our competitors, so I hope that by the time of publication in a week or so our scores will even be better. But the reality is that based on the metrics above, our link index quality, quantity, and speed are excellent. I’m not going to say our index is the best. I don’t think that’s something anyone can really even know and is highly dependent upon the specific use case. But I can say this — it is damn good. In fact, Moz has won or tied for the “gold” 27 out of the last 30 days.
What’s next?
We are going for gold. All gold. All the time. There’s a ton of great stuff on the horizon. Look forward to regular additions of features to Link Explorer based on the data we already have, faster crawling, and improved metrics all around (PA, DA, Spam Score, and potentially some new ones in the works!) There’s way too much to list here. We’ve come a long way but we know we have a ton more to do. These are exciting times!
A bit about DA and PA
Domain Authority and Page Authority are powered by our link index. Since we’re moving from an old, much smaller index to a larger, much faster index, you may see small or large changes to DA and PA depending on what we’ve crawled in this new index that the old Mozscape index missed. Your best bet is just to compare yourselves to your competitors. Moreover, as our index grows, we have to constantly adjust the model to address the size and shape of our index, so both DA and PA will remain in beta a little while. They are absolutely ready for primetime, but that doesn’t mean we don’t intend to continue to improve them over the next few months as our index growth stabilizes. Thanks!
Quick takeaways
Congratulations for getting through this post, but let me give you some key takeaways:
- The new Moz Link Explorer is powered by an industry-leading link graph and we have the data to prove it.
- Tell your data providers to put their math where their mouth is. You deserve honest, well-defined metrics, and it is completely right of you to demand it from your data providers.
- Doing things right requires that we sweat the details. I cannot begin to praise our leadership, SMEs, designers, and engineers who have asked tough questions, dug in, and solved tough problems, refusing to build anything but the best. This link index proves that Moz can solve the hardest problem in SEO: indexing the web. If we can do that, you can only expect great things ahead.
Thanks for taking the time to read! I look forward to answering questions in the comments or you can reach me on Twitter at @rjonesx.
Also, I would like to thank the non-Mozzers who offered peer reviews and critiques of this post in advance — they do not necessarily endorse any of the conclusions, but provided valuable feedback. In particular, I would like to thank Patrick Stox of IBM, JR Oakes of Adapt Partners, Alexander Darwin of HomeAgency, Paul Shapiro of Catalyst SEM, the person I most trust in SEO, Tony Spencer, and a handful of others who wished to remain anonymous.
http://tracking.feedpress.it/link/9375/9020834?utm_medium=feed&utm_source=feedpress.me&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+mozblog

